Abstract: This article provides a comprehensive guide on common questions regarding Tape and Reel Machines in SMT/EMS production. It covers operational methods, maintenance SOPs, troubleshooting, and optimization tips, suitable for production engineers and equipment procurement professionals.
Table of Contents
- Tape and Reel Machine Introduction
- Core Components and Working Principles
- Tape Loading Operation Steps
- Reel Loading Operation Guide
- Common Operational Problems and Solutions
- Maintenance and Care SOP
- Efficiency Optimization Tips
- Safety Operation Notes
- Common Troubleshooting and Handling
- Procurement Considerations for Tape and Reel Machines
- Conclusion
1. Tape and Reel Machine Introduction
Tape and Reel Machines are essential in modern SMT production lines. Their main function is to place SMD components into carrier tapes (Tape) and then wind them into standard reels (Reel) for easy handling by pick-and-place machines.
Using tape and reel machines significantly improves production efficiency, reduces manual errors, and ensures component safety during transport and storage. Different models suit different component sizes (0201, 0402, 0603) and support multiple tape widths and reel specifications, from small lab batches to high-volume production lines.
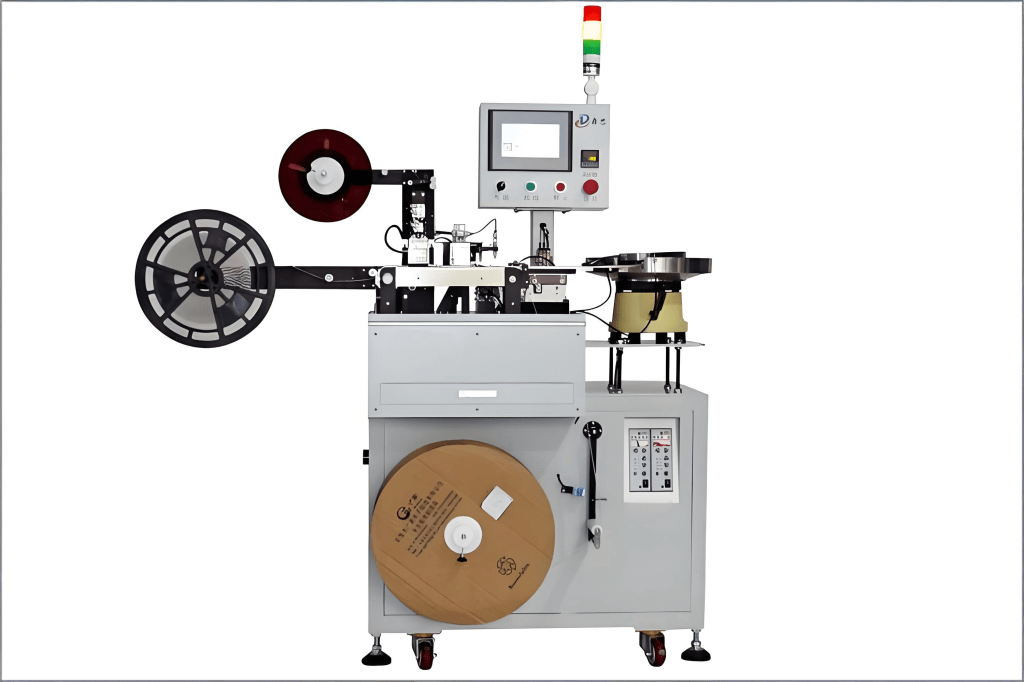
2. Core Components and Working Principles
- Main Unit: Frame, motors, control system – the core driving force.
- Feeding Mechanism: Moves the carrier tape to the filling position, typically using stepper motors and tension adjustment devices.
- Reel Device: Collects completed tapes into reels with uniform tension.
- Inspection Module: Optical sensors or cameras detect component positions and quantities to prevent skips or losses.
Working Principle: Components are placed in tape pockets, the feeding mechanism advances the tape, the inspection module monitors positions, and the reel device winds the tape into finished reels. The system can connect to MES for real-time monitoring and quality control.
3. Tape Loading Operation Steps
- Material Preparation: Check tape width and component specifications; verify quantity and batch number; clean tape surface.
- Tape Installation: Fix the tape on the feeder; adjust guiding tracks; ensure tape is flat without folds.
- Tension Adjustment: Adjust stepper motor tension; test feeding smoothness; avoid slack or over-tight tension.
- Trial Run: Run a few empty cycles; check sensor detection; confirm first component placement.
4. Reel Loading Operation Guide
- Reel Selection and Inspection: Choose reel size; check for cracks or damages; match spindle.
- Loading Steps: Mount tape onto reel; secure reel; adjust tension; ensure smooth rotation.
- Tension and Calibration: Adjust tension nut; perform empty run; confirm uniform winding.
- First Component Check: Ensure correct position; no skips or misplacements; record first article inspection.
5. Common Operational Problems and Solutions
| Problem | Possible Cause | Solution |
|---|---|---|
| Feeding not smooth | Stepper motor tension incorrect | Adjust tension; clean guides |
| Tape skipping | Tape pocket size mismatch | Check tape specs; reinstall tape |
| Component loss | Sensor fault or loose tape | Check sensor; secure tape |
| Uneven reel winding | Reel tension unbalanced | Adjust reel tension nut; empty run test |
6. Maintenance and Care SOP
- Daily Check: Clean feeding guides; check motor operation; inspect sensors.
- Regular Lubrication & Cleaning: Weekly guide cleaning; lubricate moving parts; check reel bearings.
- Component Life Management: Record motor runtime; replace wear parts regularly; keep spare parts stock.
- Fault Log: Document maintenance; record anomalies and resolutions; provide reference for optimization.
7. Efficiency Optimization Tips
- Auto-parameter adjustment based on component size.
- MES integration for real-time monitoring and alerts.
- Reduce component loss by optimizing first-article testing and tension.
- Production and yield optimization: optimize feeder mechanism to reduce downtime and improve throughput by 15%.
8. Safety Operation Notes
- Check equipment and remove debris before operation.
- Wear ESD gloves during operation.
- Stop machine immediately on abnormalities and troubleshoot.
- Train operators and conduct periodic assessments.
9. Common Troubleshooting and Handling
| Fault | Possible Cause | Handling Method |
|---|---|---|
| Sensor alarm | Obstruction or damage | Clean or replace sensor |
| Motor anomaly | Voltage instability or wear | Check power; repair motor |
| Software alarm | Parameter mismatch | Correct parameters; restart system |
10. Procurement Considerations for Tape and Reel Machines
- Brand and Manufacturer: Prefer China Manufacturer/Supplier for cost-effectiveness and after-sales.
- Price and Value: Choose model according to production line capacity.
- After-Sales and Spare Parts: Ensure quick response and spare part supply.
- Production Line Compatibility: Tape width, reel size, supported component dimensions.
11. Conclusion
Tape and Reel Machines are critical for SMT production efficiency and yield. Proper operation, maintenance, and optimization are key to ensuring long-term production performance. By following standardized procedures, conducting regular maintenance, and leveraging intelligent optimization, downtime and component loss can be minimized, resulting in higher throughput and improved production quality.







留下评论